Acid Reflux Diet⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide provides valuable information on acid reflux, its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies, including dietary modifications and lifestyle changes. It delves into the crucial role of diet in controlling acid reflux symptoms, offering a detailed list of foods to avoid and foods to include in your diet for optimal results. You’ll find a sample acid reflux diet meal plan to help you navigate your dietary choices effectively. This guide empowers you to take control of your acid reflux and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable life.
What is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux, also known as heartburn, is a common condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. This backflow of acid can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing a burning sensation in the chest, often referred to as heartburn. While occasional acid reflux is normal, frequent or persistent reflux can lead to a more serious condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a muscle that acts like a valve, preventing stomach acid from flowing back up into the esophagus. When this muscle relaxes or weakens, it allows stomach contents to flow back upward, causing acid reflux. Various factors can contribute to LES weakness, including⁚
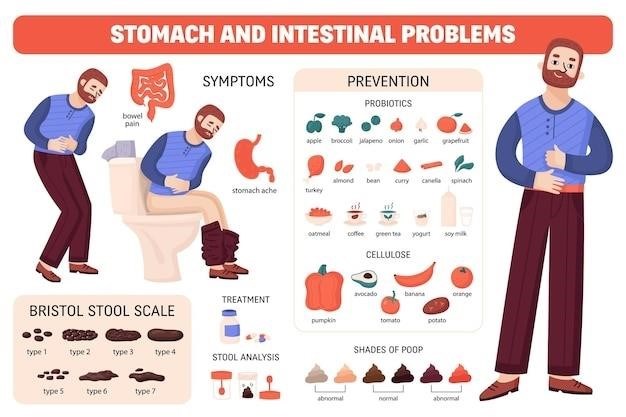
- Overeating⁚ Eating large meals can put pressure on the LES, increasing the risk of reflux.
- Certain foods and drinks⁚ Some foods and drinks can relax the LES or increase acid production in the stomach, making reflux more likely.
- Obesity⁚ Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach and LES, increasing the risk of reflux.
- Pregnancy⁚ Hormonal changes during pregnancy can relax the LES, increasing the risk of reflux.
- Smoking⁚ Smoking can damage the LES, making it more likely to relax.
- Certain medications⁚ Some medications, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and some anti-anxiety drugs, can relax the LES.
- Hiatal hernia⁚ A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest and abdomen. This can weaken the LES and increase the risk of reflux.
If you experience frequent or persistent acid reflux, it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Common Symptoms of Acid Reflux
Acid reflux can manifest in various ways, and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for effective management. The most common symptom is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest that can radiate up into the throat. This discomfort often worsens after eating, especially large meals, lying down, or bending over.
In addition to heartburn, other common symptoms of acid reflux include⁚
- Sour or bitter taste in the mouth⁚ This occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the throat and mouth.
- Regurgitation⁚ This is the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus and mouth, often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste.
- Difficulty swallowing⁚ Stomach acid can irritate the esophagus, making swallowing uncomfortable or painful.
- Chronic cough⁚ Persistent acid reflux can trigger a chronic cough as the body tries to clear the irritation.
- Hoarseness or sore throat⁚ Stomach acid can irritate the vocal cords, causing hoarseness or a sore throat.
- Wheezing or asthma⁚ In some cases, acid reflux can trigger or worsen asthma symptoms.
- Dental problems⁚ Chronic acid reflux can erode tooth enamel, leading to dental issues.
- Chest pain⁚ Acid reflux can sometimes mimic chest pain associated with heart problems. If you experience chest pain, it’s essential to see a doctor to rule out any serious heart conditions.
If you experience any of these symptoms frequently or persistently, it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications associated with acid reflux.
The Role of Diet in Managing Acid Reflux
Diet plays a crucial role in managing acid reflux symptoms and is often the first line of therapy for individuals with GERD; By making strategic dietary changes, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of heartburn and other reflux-related discomforts.
Here’s how diet impacts acid reflux⁚
- Trigger Foods⁚ Certain foods and beverages can trigger or worsen acid reflux. These foods often relax the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally prevents stomach acid from flowing back up into the esophagus. Trigger foods can also increase the production of stomach acid, contributing to reflux.
- Dietary Management⁚ By identifying and avoiding trigger foods, you can effectively manage acid reflux symptoms. A well-planned diet can help prevent the relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, minimize stomach acid production, and promote quicker digestion, all of which contribute to reducing reflux episodes.
- Nutritional Considerations⁚ Beyond simply avoiding trigger foods, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides essential nutrients and can support overall digestive health.
While dietary changes can be highly effective, it’s important to note that they may not be sufficient for everyone. If you experience persistent or severe acid reflux, consult a doctor for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan that may include medications or other interventions.
Foods to Avoid for Acid Reflux
While a healthy diet is essential for managing acid reflux, certain foods can trigger or worsen symptoms. These foods often share characteristics that make them particularly problematic for individuals with GERD.
Here are some of the most common foods to avoid⁚
- Fatty Foods⁚ Fatty foods take longer to digest, which can increase pressure in the stomach and lead to reflux. Examples include fried foods, fatty meats, and full-fat dairy products.
- Citrus Fruits and Juices⁚ The acidity of citrus fruits and juices can irritate the esophagus and trigger heartburn. Examples include oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes.
- Chocolate⁚ Chocolate contains theobromine, a stimulant that can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to back up into the esophagus.
- Garlic and Onions⁚ These pungent ingredients can irritate the stomach and worsen reflux symptoms.
- Spicy Foods⁚ Spicy foods, particularly those containing chili peppers, can increase stomach acid production and lead to heartburn.
- Tomato Products⁚ Tomatoes are naturally acidic and can irritate the esophagus, contributing to reflux symptoms.
- Alcohol⁚ Alcohol can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, increase stomach acid production, and irritate the esophagus.
- Caffeine⁚ Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and soda, can also relax the lower esophageal sphincter and increase stomach acid production.
- Mint⁚ While often enjoyed for its refreshing flavor, mint can relax the lower esophageal sphincter and worsen reflux symptoms.
It’s important to note that individual tolerance to these foods can vary. Keep a food diary to identify your personal triggers and make adjustments to your diet accordingly.
Foods to Include in Your Diet
While avoiding trigger foods is crucial for managing acid reflux, incorporating foods that promote digestive health and soothe the esophagus is equally important. These foods can help neutralize stomach acid, strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter, and promote overall digestive well-being.
Here are some foods that are generally considered safe and beneficial for individuals with acid reflux⁚
- Lean Protein⁚ Lean protein sources like chicken breast, fish, beans, and tofu are easy to digest and don’t trigger reflux. They also help you feel full and satisfied, which can prevent overeating.
- Whole Grains⁚ Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are rich in fiber, which helps regulate digestion and prevent acid reflux.
- Non-Acidic Fruits⁚ Choose fruits that are lower in acidity, such as bananas, melons, and pears. These fruits provide essential vitamins and minerals without exacerbating your symptoms.
- Green Leafy Vegetables⁚ Green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and lettuce are low in acid and rich in fiber, making them excellent choices for individuals with acid reflux.
- Ginger⁚ Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory and can help soothe the digestive tract. It can be enjoyed in tea, stir-fries, or as a supplement.
- Chamomile Tea⁚ Chamomile tea has calming properties and can help relax the digestive system, reducing the risk of reflux.
- Probiotic Foods⁚ Probiotic foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain beneficial bacteria that can improve gut health and digestion. They can help regulate stomach acid levels and promote a healthy digestive system.
Remember to eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals to reduce pressure on the stomach. And stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Sample Acid Reflux Diet Meal Plan
This sample meal plan provides a framework for a 7-day acid reflux diet. It emphasizes incorporating foods that are generally considered safe and beneficial for individuals with acid reflux, while limiting or avoiding trigger foods. Remember, individual needs and tolerances may vary, so it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that aligns with your specific health needs.
Here’s a sample meal plan you can follow⁚
Day 1
- Breakfast⁚ Oatmeal with berries and a sprinkle of nuts
- Lunch⁚ Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cucumber, and avocado dressing
- Dinner⁚ Baked salmon with roasted broccoli and brown rice
- Snacks⁚ Banana, plain yogurt with chia seeds
Day 2
- Breakfast⁚ Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole wheat toast
- Lunch⁚ Lentil soup with a side of whole grain bread
- Dinner⁚ Turkey meatballs with spaghetti squash and marinara sauce
- Snacks⁚ Pear, almonds
Day 3
- Breakfast⁚ Smoothie with banana, spinach, and almond milk
- Lunch⁚ Quinoa salad with chickpeas, bell peppers, and a lemon vinaigrette
- Dinner⁚ Chicken stir-fry with brown rice and vegetables
- Snacks⁚ Apple slices, plain yogurt
Day 4
- Breakfast⁚ Greek yogurt with berries and granola
- Lunch⁚ Leftover chicken stir-fry
- Dinner⁚ Tofu scramble with bell peppers, onions, and whole wheat tortillas
- Snacks⁚ Carrot sticks, hummus
Day 5
- Breakfast⁚ Whole wheat toast with avocado and a poached egg
- Lunch⁚ Tuna salad sandwich on whole grain bread with lettuce and tomato
- Dinner⁚ Vegetarian chili with brown rice
- Snacks⁚ Grapes, plain yogurt
Day 6
- Breakfast⁚ Oatmeal with chia seeds and a banana
- Lunch⁚ Leftover vegetarian chili
- Dinner⁚ Baked chicken breast with roasted sweet potatoes and green beans
- Snacks⁚ Celery sticks with peanut butter, almonds
Day 7
- Breakfast⁚ Scrambled eggs with mushrooms and whole wheat toast
- Lunch⁚ Salad with black beans, corn, and a light vinaigrette
- Dinner⁚ Lentil and vegetable curry with brown rice
- Snacks⁚ Apple slices with cinnamon, plain yogurt with berries
This sample meal plan offers a starting point. Adjust it based on your preferences and dietary needs. Remember to eat slowly, chew your food thoroughly, and avoid large meals to minimize pressure on your stomach and reduce the risk of reflux.
Lifestyle Modifications for Acid Reflux
While diet plays a crucial role in managing acid reflux, making certain lifestyle changes can significantly enhance your efforts. These adjustments help create a more favorable environment for your digestive system and reduce the likelihood of reflux episodes. Adopting these habits alongside dietary modifications can contribute to a noticeable improvement in your overall well-being and a reduction in acid reflux symptoms.
Here are some key lifestyle modifications to consider⁚
- Weight Management⁚ Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce pressure on your stomach and lower the risk of acid reflux. If you are overweight or obese, even a modest weight loss can make a noticeable difference.
- Elevate Your Head⁚ Raising your head and upper body while sleeping can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into your esophagus. Use an extra pillow or adjust your bed frame slightly to achieve a comfortable incline.
- Avoid Tight Clothing⁚ Tight clothing around your abdomen can put pressure on your stomach and contribute to acid reflux. Opt for loose-fitting garments, especially after meals.
- Limit Alcohol and Smoking⁚ Alcohol and smoking can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the risk of reflux. Limit your intake of alcohol and avoid smoking altogether.
- Eat Smaller Meals More Frequently⁚ Large meals put significant pressure on your stomach. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help keep your stomach from becoming overly full, reducing the chances of reflux.
- Avoid Eating Before Bed⁚ Give your body time to digest food before lying down. Try to avoid eating at least 2-3 hours before bedtime to minimize the risk of nighttime reflux.
- Manage Stress⁚ Stress can contribute to digestive issues, including acid reflux. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature.
By implementing these lifestyle changes alongside dietary modifications, you can effectively manage acid reflux and improve your overall digestive health.